How to Pass the OLSAT Test Level B and OLSAT Level C in 2024
Updated January 29, 2024
What Is the OLSAT?
The Otis–Lennon School Ability Test (OLSAT) is widely used in US schools to measure your child’s educational progress compared with other children of their age. It is also used to identify gifted and talented children.
OLSAT is a multiple-choice test that includes questions on verbal, non-verbal, pictorial, figural and quantitative reasoning.
OLSAT is available across the entire school age range, from kindergarten to 12th grade.
The content of each OLSAT test is on a grade level and is relevant to the age and school year it is aimed at. Level B is aimed at 1st graders who are around six years old. Level C is aimed at 2nd graders who are seven years old.
What to Expect on the OLSAT 8 Level C and B Tests
OLSAT is a multiple-choice test that varies in its exact content, depending on the grade. Level B and C questions are split between verbal and non-verbal and will assess a child’s pictorial, figural and quantitative reasoning.
Similar to the CogAT, the OLSAT is assesses reasoning skills using different types of questions, but has two sections rather than three.
OLSAT is generally taken in a group setting and is available online or in a pencil and paper format, depending on the age of the child.
Level B OLSAT
The Level B OLSAT is designed for 1st graders. It includes 60 questions, of which 30 are verbal and 30 are non-verbal. There is a time limit of 77 minutes to complete the test.
The questions and related guidance are read aloud to the children in English. However, should your child not be confident in their English language skills, it is possible to take the OLSAT in another language.
Level B OLSAT questions cover the following topics:
- Following directions
- Aural reasoning
- Arithmetic
- Picture classification
- Picture analogies
- Figural classification and analogies
- Pattern matrix
- Figural series
Practice OLSAT Level B with Test Prep Online
Level C OLSAT
The Level C OLSAT is aimed at children in the 2nd grade. The difference in age is reflected in the increased difficulty and breadth of the test questions. As the majority of children in this grade will be able to read, only half of the questions will be read out by the teacher.
Your child will be expected to answer the remaining questions independently. Level C includes 60 questions – 30 verbal and 30 non-verbal – but the time limit for the test is shorter than Level B, at 72 minutes.
Level C OLSAT questions cover the same topics as the Level B test. It is still advised to make use of OLSAT level C practice tests before taking the actual exam.
Practice OLSAT Level C with Test Prep Online
OLSAT Test Score Interpretation
The OLSAT is scored by comparing your child’s test score with that of their peer group. Your child’s OLSAT score is presented in three ways:
- Raw score – The total number of questions that your child has answered correctly, for instance, 48 out of 60.
- School ability index (SAI) score – Your child’s raw score is assessed using the SAI scale to compare it to similarly aged children and arrive at a normalized score. The average SAI is 100.
- Percentile rank – The SAI score is converted into a percentile rank by comparing it to the SAI results of children within the same age group.
Unlike many academic tests, there is no pass or ‘good’ score for the OLSAT. This test is designed to assess your child’s current level of learning and calculate how they compare to others of a similar age.
However, eligibility for most gifted and talented programs relies on a minimum SAI score of 132.
OLSAT Practice test 2nd Grade & 1st Grade: Sample Questions (2024)
Verbal Comprehension
In the verbal comprehension section, your child will face ‘following directions’ questions. The aim of this type of question is to assess:
- Whether your child can listen to and interpret instructions
- Your child’s ability to understand relational terms, such as ‘beside’ or ‘behind’
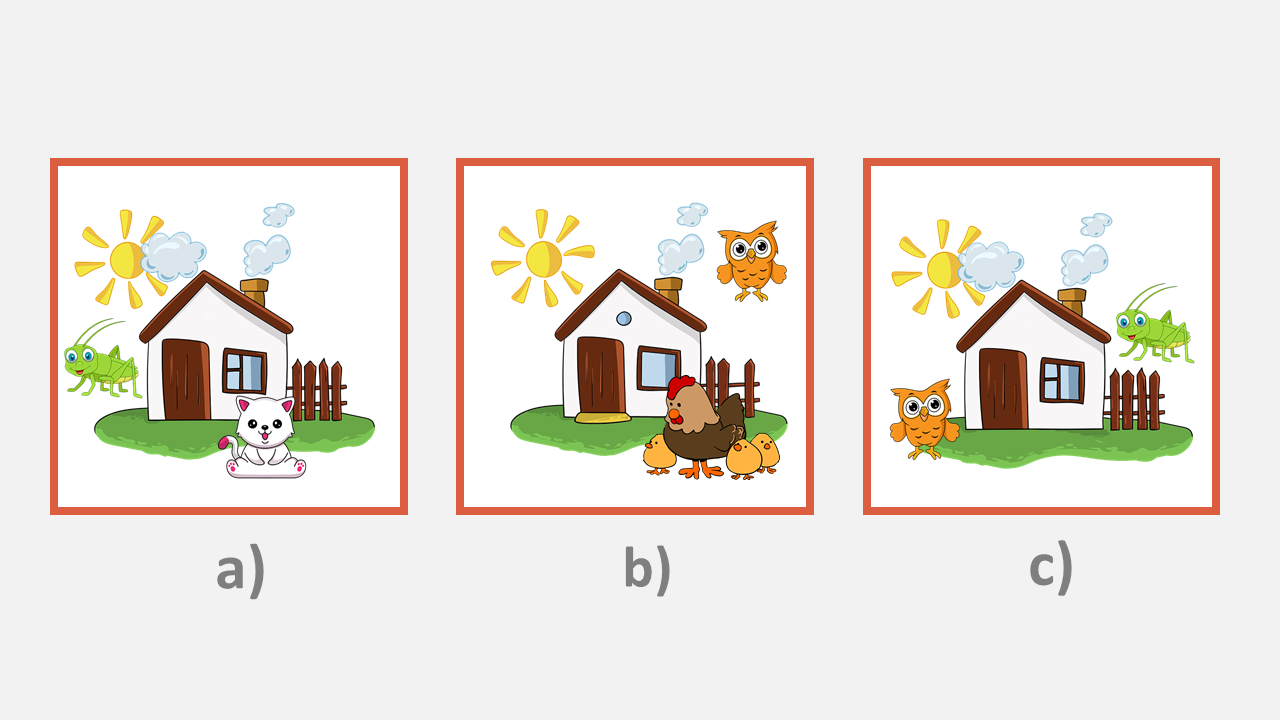
Which picture has three clouds, an owl and a grasshopper?
Verbal Reasoning
In this section of the test, your child will face aural reasoning and arithmetic reasoning questions:
- Aural reasoning questions – Assesses how well your child can listen to and interpret separate pieces of information to reach a conclusion.
- Arithmetic reasoning questions – Assesses problem-solving skills with a focus on numeracy and logic.
Sample Aural Reasoning Question
If you want 12-month access to all the practice resources for this test, our partner TestPrep-Online.com offers a Family Membership.
Family Membership gives you access to all the TestPrep-Online resources for the next 12 months. You will also get two separate accounts, which can be very helpful if you have two children preparing for their tests.
Get a Family Membership with 12-month access
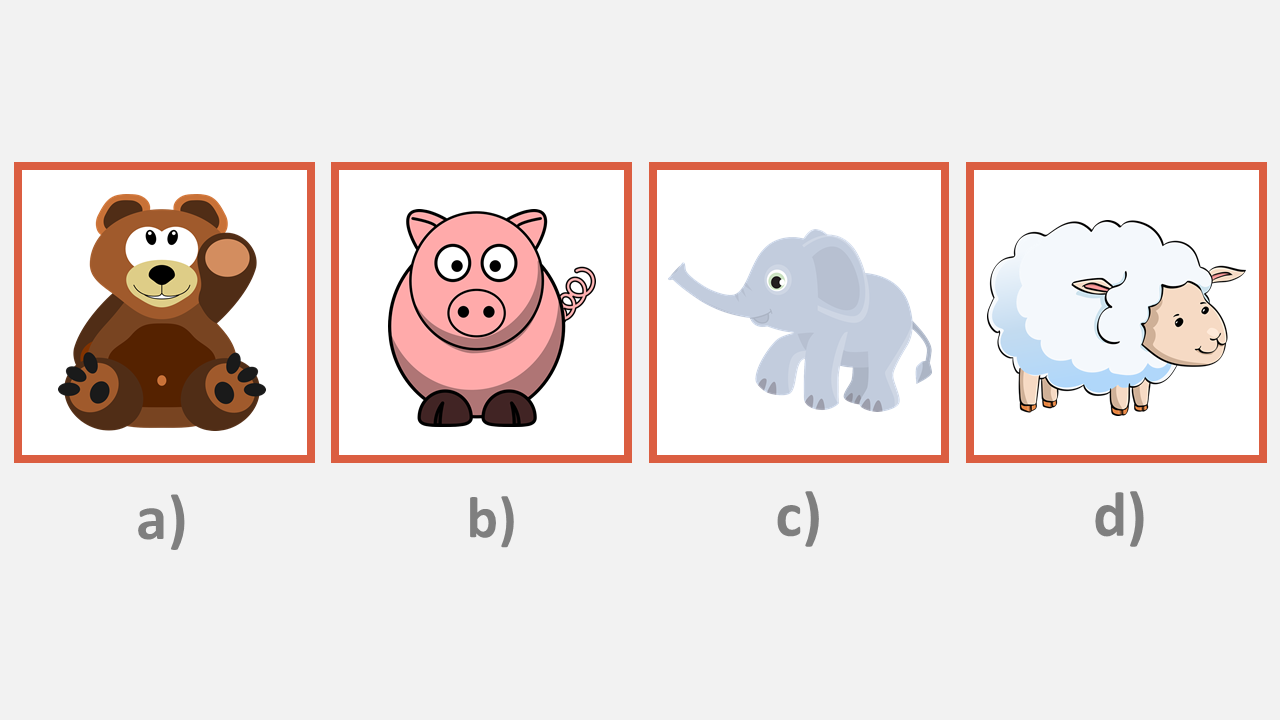
Susan has a favorite animal. It is not a farm or ranch animal. It does not have fur. It does not have wool.
Which of the pictures shows Susan’s favorite animal?
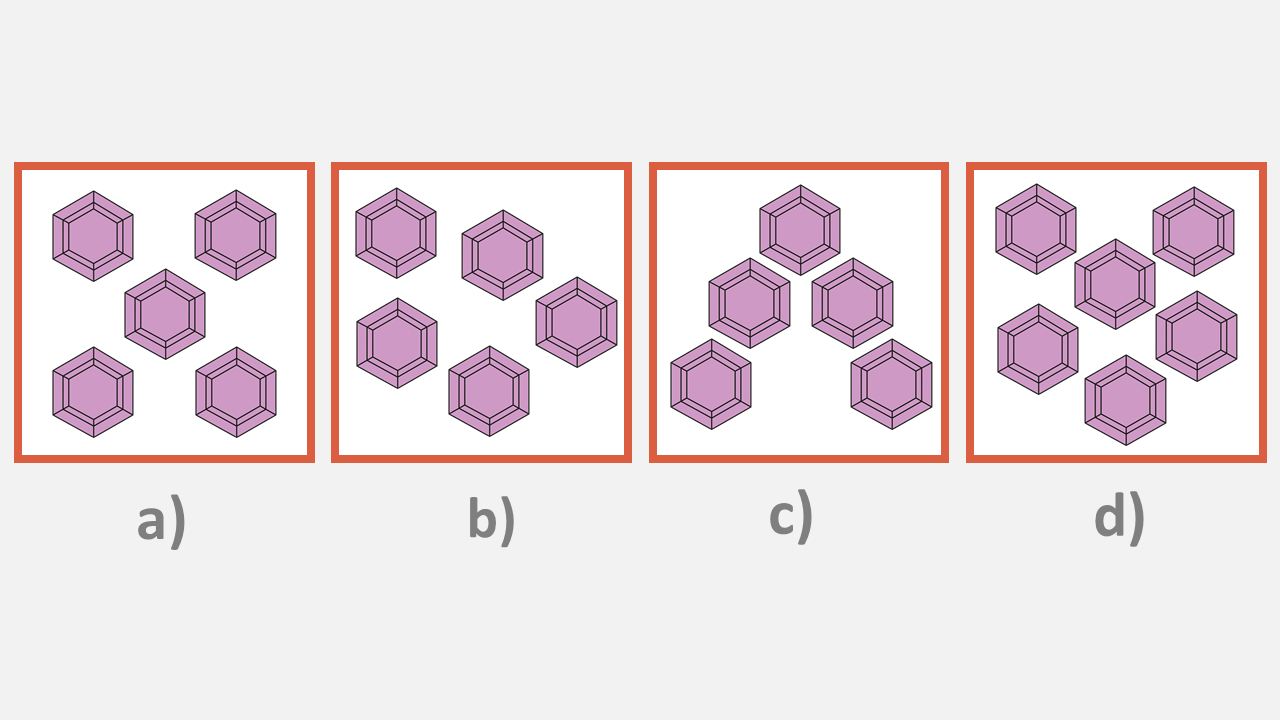
One of the following groups of shapes does not fit with the others.
Which is it?
Pictorial Reasoning
Questions in this section will include picture classification and picture analogies. Picture classification asks the child to identify the odd one out.
Picture analogy assesses the child’s understanding of how the provided pictures relate to each other.
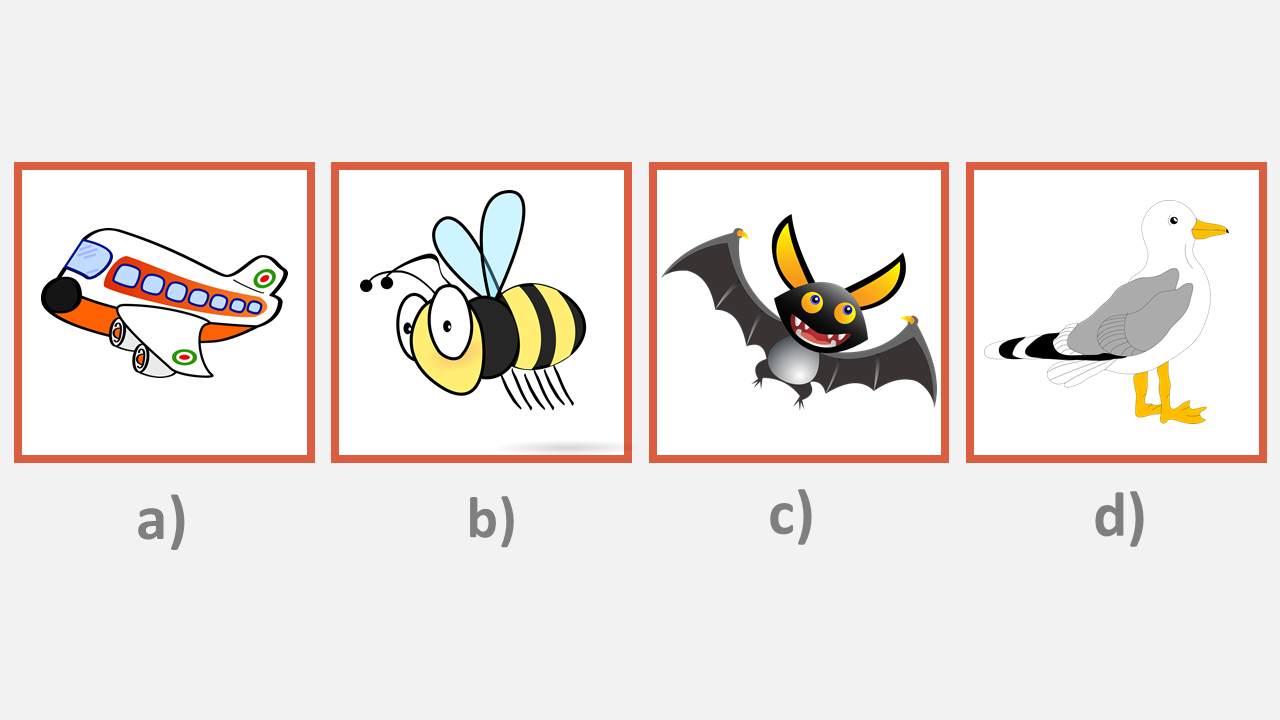
Sample Picture Classification Question
Look at the pictures below. Which one does not belong?

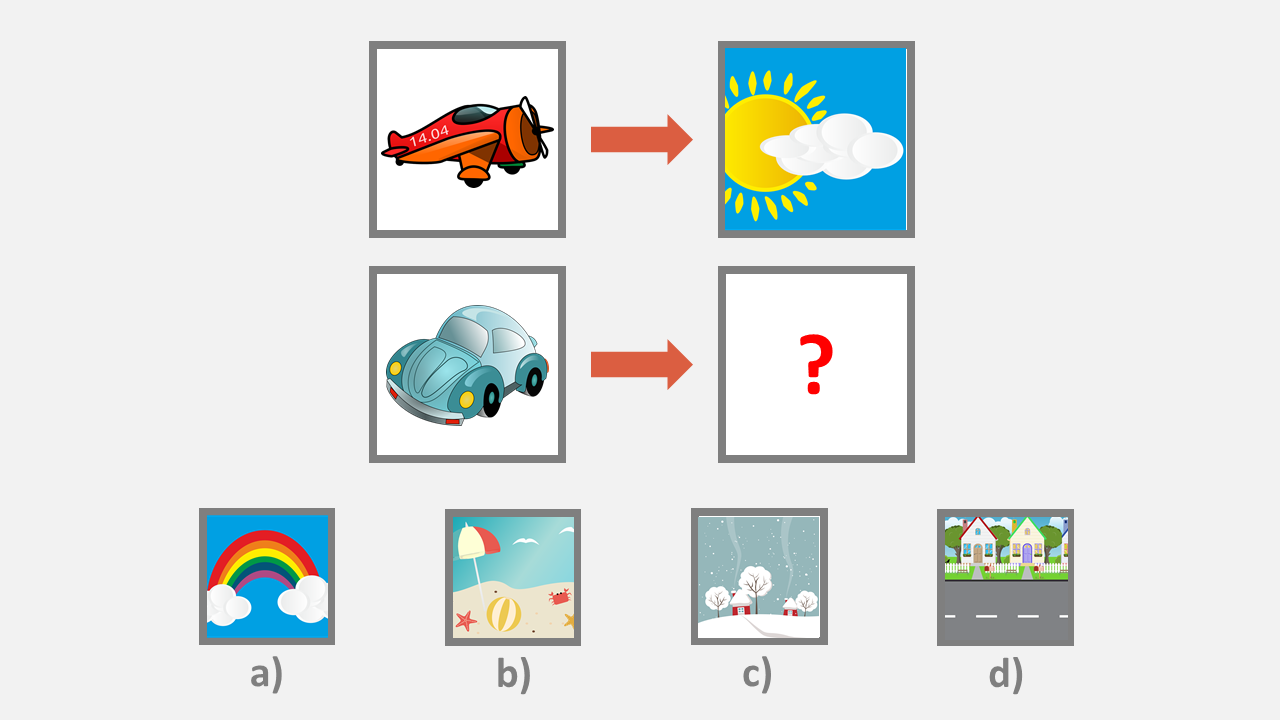
The pictures in the top boxes belong together in a certain way. What belongs to the bottom picture in the same way that the pictures on the top belong together?

Figural Reasoning
This section of the OLSAT test includes questions on:
- Figural classification – Asks for the odd one out
- Figural analogy – Assesses the child’s ability to identify relationships between items
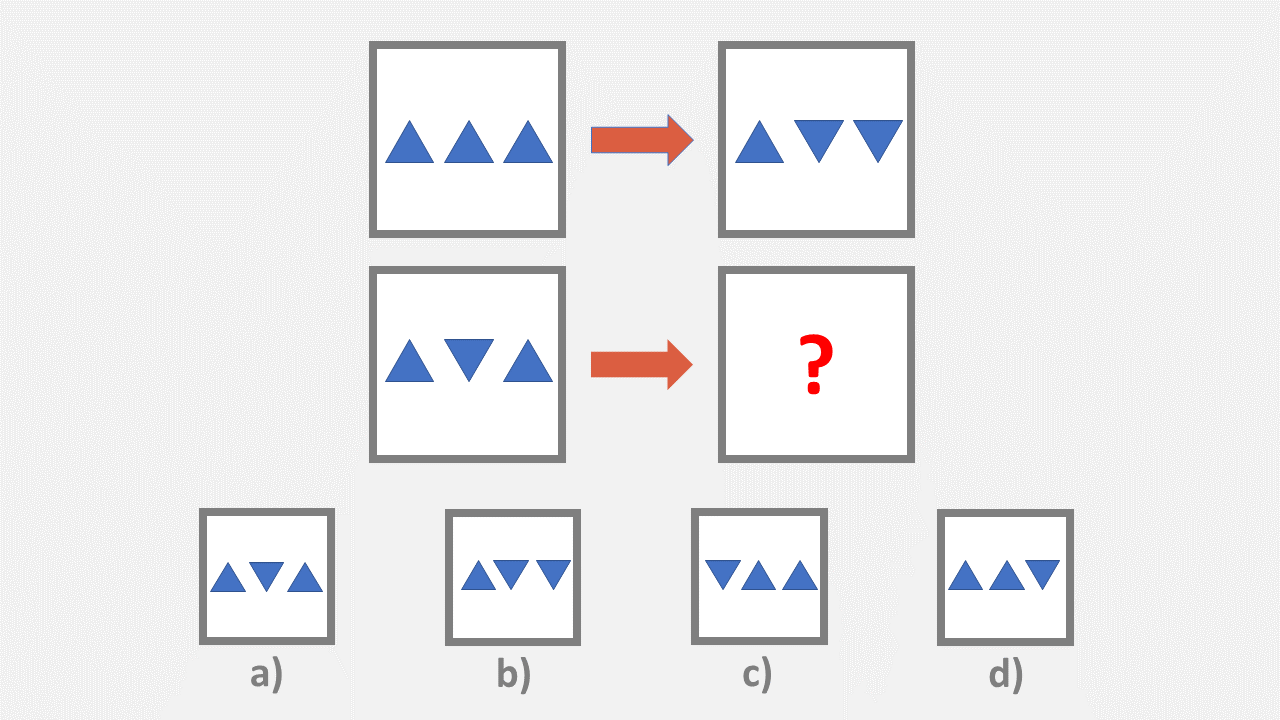
- Pattern matrix – Asks for the missing item to be provided
- Figural series – Assesses how well the child can identify the next item in a series
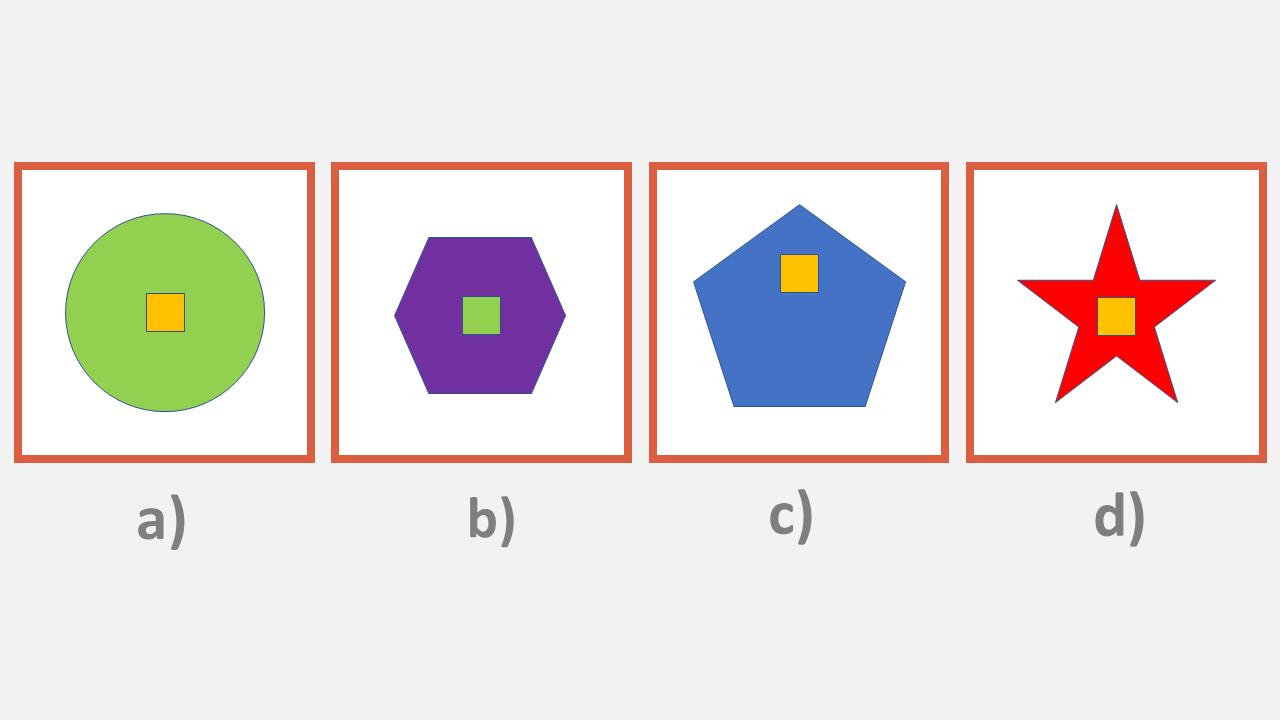
Sample Figural Classification Question
Look at the shapes below. Which does not belong?
The shapes in the top boxes go together in a certain way. What belongs to the bottom set of shapes in the same way that the shapes on the top go together?
OLSAT Test Prep 2nd Grade & 1st Grade in 2024
As with any school test, the key to the best performance is preparation. There are many ways that you can help your child prepare for the OLSAT Level B or Level C test.
Read on for our step-by-step tips:
Step 1. Use Practice Papers
Your child will feel more confident about taking tests if they know what type of questions they will face. This is where practice papers can be useful.
Your child’s teacher may provide practice papers and sample questions, but they can also be sourced online. For instance, the following sites can provide an OLSAT practice test (1st grade & 2nd):
Step 2. Work With Your Child’s Teacher
You know your child best, but their teacher spends a lot of time with them each week. Work with the teacher to develop a bigger picture of your child’s progress.
Do they have any concerns about areas that need more work, such as verbal comprehension or figural problem-solving? Can they provide practice materials and guidance?
Be open to what the teacher has to say so that you can work together to support your child’s development.
Step 3. Work Through Practice Questions With Your Child
Help your child to understand how to approach the OLSAT test by working through practice questions with them at the start.
This will increase their confidence, allow them to develop test-taking strategies – more of that below – and help you to understand where their strengths and weaknesses lie.
Eventually, your child will be confident enough to work on practice questions on their own.
Step 4. Develop Test-Taking Strategies
Success in test-taking is as much about how your child approaches the questions as their academic abilities. Talk to them about how they might tackle each question.
For instance:
- Eliminating the answers your child knows are incorrect to narrow down the number of possible right answers
- Reading the question and answers carefully before attempting to work out what the correct answer is
- Trying out answers to see if they fit before deciding which one is right
A study guide might also be great test preparation.
Step 5. Be Positive
At such a young age, test-taking can be overwhelming. Refrain from adding any undue pressure on your child by keeping upbeat when talking to them about the OLSAT.
Acknowledge that they will be taking the test, express your confidence in their abilities and try not to let the upcoming test take over your life and your child's.
Step 6. Safeguard Your Child’s Health
You can also prepare your child for test-taking by making sure they are healthy. That means:
- Getting enough sleep
- Eating a nutritionally balanced diet – not too much of anything and not too little, either
- Drinking plenty of water to prevent dehydration
- Staying active
- Boosting their confidence through positive, constructive communication and family time
The OLSAT is widely considered to be a reliable and valid way to assess levels of learning and gain admission into gifted and talented school programs.
Levels B and C provide early indications of where a child’s strengths and weaknesses lie in comparison to their peers.
Level B and Level C of the OLSAT test are designed to be relevant for the learning progress of 1st and 2nd graders.
This means that OLSAT test questions will challenge your child, but it is possible to do well.
OLSAT 8 (level C or B) is a multiple-choice test that is made up of verbal and non-verbal questions.
Questions in both Level B and C cover verbal comprehension, verbal reasoning, arithmetic reasoning, pictorial reasoning and figural reasoning.
There is no good score for the OLSAT Level B or C. The test is designed to assess your child’s standard of learning and compare their score to other children of a similar age.
The average SAI score is 100. Eligibility for most gifted and talented programs relies on a minimum SAI score of 132.
Yes, your child is allowed to prepare for the OLSAT test. Your child’s teacher may provide practice materials and guides. OLSAT 8 practice tests and sample questions can also be sourced online.
Work with your child’s teacher to build a clear picture of your child’s progress, strengths and weaknesses. Source OLSAT 8 practice tests and work with your child on practice questions to get them started.
Help them develop test-taking strategies. Most important of all, be supportive of your child.
You will generally receive a detailed score report in the post around two months after your child takes the OLSAT 2nd grade or 1st grade test.
Final Thoughts
The OLSAT is a widely recognized assessment of learning ability for school children from kindergarten to 12th grade and is used as an admission tool by many talented and gifted school programs.
OLSAT Levels B and C are taken by children in 1st and 2nd grade, respectively.
As a parent, you have the opportunity to support your child to achieve their best score. Help them to prepare by using practice papers to familiarize themselves with the test format, build their confidence and reduce test-taking nerves.






